Inpixon's advanced location engine software for both ultra-wideband (UWB) and chirp (CSS) RTLS deployments processes thousands of concurrently received location blinks from RTLS tags to monitor their movements in real-time, delivering actionable intelligence. Inpixon's location engine helps automate tracking of the current location, status, and interactions of people and objects throughout facilities and can be seamlessly integrated into existing IoT infrastructures.
With its proven scalability and low latency, Inpixon's location engine takes RTLS deployments to the next level. Ideal for industrial location applications, Inpixon's location engine provides both long-range chirp and precise UWB positioning for up to thousands of concurrently tracked IoT devices. This enables RTLS solutions that can power a wide array of critical location-aware applications in many different types of environments, including finding an injured mining worker deep underground, avoiding collisions between vehicles and factory workers, monitoring parts on a product line, boosting productivity by detecting bottlenecks and process inefficiencies, activating ventilation as a worker enters an area, and more.
Precise Accuracy
Sub-nanosecond wireless anchor synchronization for precision positioning.
Scalable
Easily expand deployments on demand or in stages. Simply add anchors and tags.
Flexible
Receive, process and supply location, ranging, section and sensor data.
A location engine is the RTLS software that takes the received location blinks and IoT data collected by RTLS anchors from transmitting tags and analyzes this data to continuously pinpoint the current location of tracked tags equipped to people and objects. For example, in environments like smart factories, a location engine will calculate the real-time positions and movements of tags carried by industrial workers, enabling digital location tracking that powers critical safety use cases such as collision avoidance or safety zoning. They’ll also track key assets like production equipment, vehicles and inventories to support enterprise asset management, automation, workflow optimization and more. Other industries, like healthcare use clinical-grade RTLS to help track staff, patients and key medical equipment like defibrillators for real-time visibility that helps them deliver vital care in urgent scenarios. Deployed in cloud-based or local environments, the location engine calculates these real-time tag positions to deliver actionable location data that can be used to visualize the location of personnel and assets on a map, or integrated into IoT platforms like ERP, MES and supply chain management solutions. 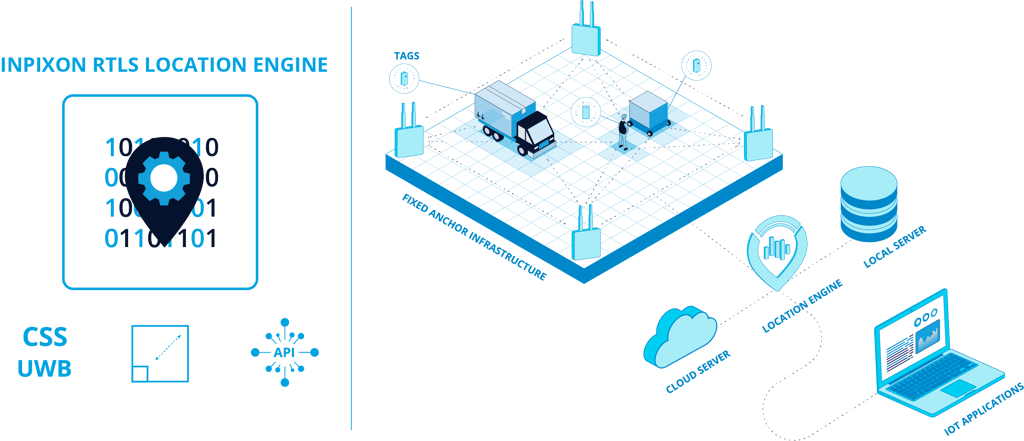
Inpixon's powerful location engine is capable of determining the real-time location of thousands of tags multiple times per second. Through mixed RF technology, the location engine enables both precise UWB and flexible, long-range chirp location tracking applications that can be combined in a single RTLS solution. Inpixon's location engine directly connects to our RTLS anchors, ingesting the complete location and sensor data-stream in real-time to calculate native TDoA-based positions of tags via precise time-of-arrival stamps (ToA). With this TDoA methodology, our patented techniques, including virtual time synchronization technology, Inpixon's location engine delivers high accuracy, superior reliability, and low-latency that support enterprise-grade tracking of personnel and key assets, especially in Industry 4.0 applications and environments where real-time visibility is paramount to safety and business results.
Inpixon's location engine supports the industrial RESTful API interface enabling simplified and standardized management of the engine and its connected infrastructure of IoT devices, anchors, tags and sensors. Built for interoperability, this RESTful API architecture allows you to seamlessly integrate location tracking capabilities into external IoT platforms and third-party systems