Technology
SDS-TWR (Symmetrical Double-Sided Two Way Ranging)
SDS-TWR stands for Symmetrical Double-Sided Two-Way Ranging:
- Symmetrical — Measurements from Station A to Station B are a mirror-image of the measurements from Station B to Station A (ABA to BAB).
- Double-sided — Two stations are used for ranging measurement
- Two-way — Two packets, a data packet and an ack packet, are used.
It is a methodology that uses two delays that naturally occur in signal transmission to determine the range between two stations. These signals are Signal Propagation Delay between two wireless devices and Processing Delay of acknowledgements within a wireless device. Because of its simple and elegant methodology, SDS-TWR can be easily adapted to many purposes, including location awareness. The following illustrates SDS-TWR.
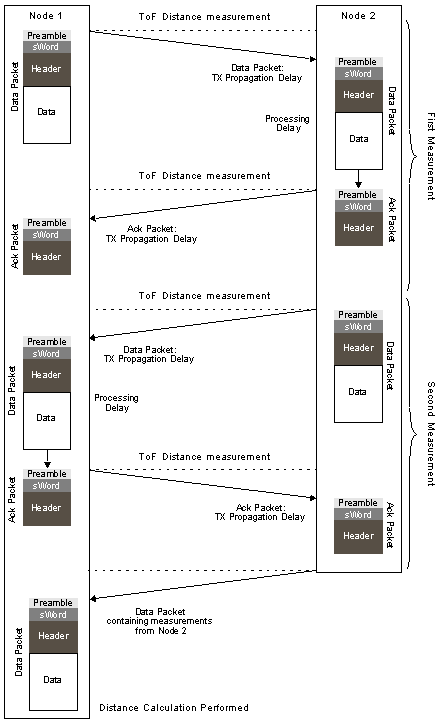
Other Features
- Signal Propagation Delay
A special type of packet (Test packets) is transmitted from Station A (Node A) to Station B (Node B). As time the packet travels through space per meter is known (from physical laws), the difference in time from when it was sent from the transmitter and received at the receiver can be calculated. This time delay is known as the Signal Propagation Delay. - Processing Delay
Station A now expects an acknowledgement from Station B. A station takes a known amount of time to process the incoming Test packet, generate an Acknowledgement (Ack packet), and prepare it for transmission. The sum of time taken to process this acknowledgement is known as Processing Delay. - Calculating the Range
The acknowledgement sent back to Station A includes in its header those two delay values – the Signal Propagation Delay and the Processing Delay. A further Signal Propagation Delay can be calculated by Station A on the received acknowledgement, even as this delay was calculated on the Test packet. These three values can then be used by an algorithm to calculate the range between these two stations. - Verifying the Range Calculation
To verify that the range calculation was accurate, the same procedure is repeated by Station B sending a Test packet to Station A and Station A sending an acknowledgement to Station B. At the end of this procedure, two range values are determined and an average of the two can be used to achieve a fairly accurate distance measurement between these two stations. - Saving Energy in Networks
Because many applications of wireless networks require long battery lifetime and low power, including ranging applications, Nanotron Technologies has developed an energy management system: EBM (Energy Budget Management).
